Total Synthesis of Myxobacterial Metabolites
Over the past three decades, isolation chemists have identified myxobacterium as a source of biologically active secondary metabolites. In addition to their pronounced activity, these metabolites posses structurally complex molecular architecture, capturing the imagination of many synthetic groups around the world. To this end our group has developed a successful research program towards synthesising these natural products. Many of them have succumbed to synthesis within our group, and along the way we have developed novel methodologies, and reassessed the original structural assignment.1–8
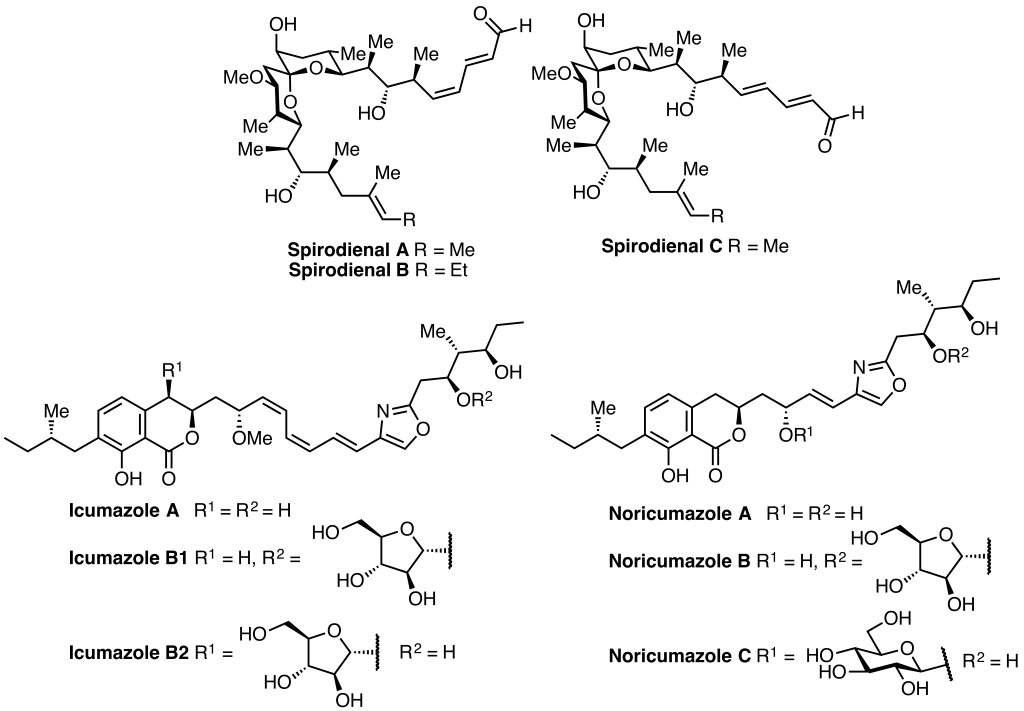
At the moment our group is interested in completing the total synthesis of the spirodienal, icumozole and noricumazole families of myxobacterial natural products.
(1) Feutrill, J. T.; Lilly, M. J.; Rizzacasa, M. A. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 3365–3367. (2) Feutrill, J. T.; Lilly, M. J.; Rizzacasa, M. A. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 525–527. (3) Hilli, F.; White, J. M.; Rizzacasa, M. A. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 1289–1292. (4) Birkett, S.; Ganame, D.; Hawkins, B. C.; Meiries, S.; Quach, T.; Rizzacasa, M. A. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1964–1967. (5) Birkett Stephen L; Loits Darran A; Wimala Samantha; Rizzacasa Mark A. Pure and Applied Chemistry . 2012, 1421-1433. (6) Birkett, S.; Ganame, D.; Hawkins, B. C.; Meiries, S.; Quach, T.; Rizzacasa, M. A. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 116–123. (7) Gregg, C.; Gunawan, C.; Ng, A. W. Y.; Wimala, S.; Wickremasinghe, S.; Rizzacasa, M. A. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 516–519. (8) Bender, T.; Loits, D.; White, J. M.; Rizzacasa, M. A. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 1450–1453.